As the COVID-19 pandemic continues, understanding the diverse testing options is vital for effective management and control of the virus spread. Diagnostic and antibody tests play unique roles, with molecular tests such as PCR standing out for accuracy, and antigen tests offering quick results despite limitations. The evolution of testing technology, including innovations for detecting variants, signifies the ongoing efforts to enhance the efficacy and accessibility of COVID-19 tests globally.
Understanding Different Types of COVID-19 Tests
Amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, a variety of testing options have emerged as essential tools in managing and controlling the spread of the virus. The two primary categories of COVID-19 tests are diagnostic and antibody tests as outlined by the FDA.
While diagnostic tests, which include molecular and antigen tests, focus on detecting an active infection, antibody tests identify past exposure to the virus.
In-Depth Look at Diagnostic Tests
Diagnostic tests can be further divided into two main types: molecular and antigen tests. Molecular tests, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests, are recognized for their sensitivity and reliability. They detect the virus’s RNA and are primarily processed in certified laboratories, which may take from one to seven days for results.
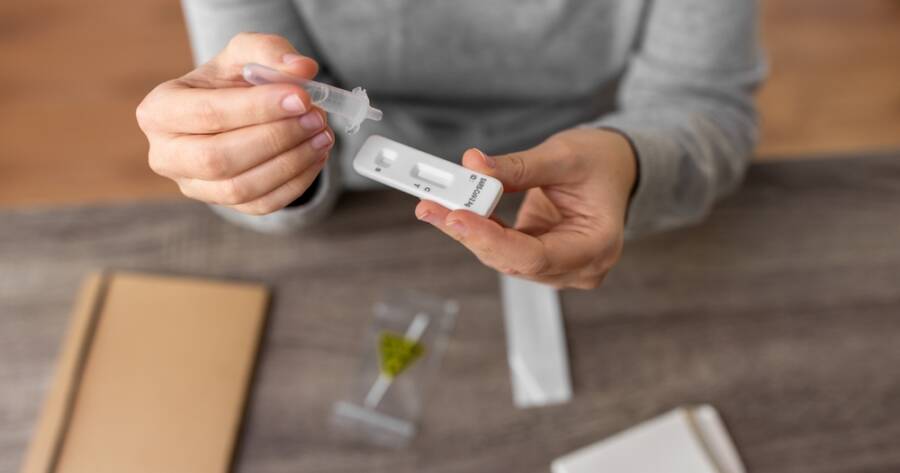
On the other hand, antigen or “rapid” tests, are designed for speed and ease of use. They are often carried out at healthcare locations or at home, delivering results in approximately 10 to 30 minutes. However, they require a higher level of viral presence in samples, making them less reliable than molecular tests, especially for individuals without symptoms according to Johns Hopkins Public Health.
The Role of Molecular Tests
Molecular tests like PCR and Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) are often considered the “gold standard” in COVID-19 testing due to their high accuracy. These tests use specific processes to detect the genetic material of the virus as the CDC indicates. Despite being time-intensive and requiring skilled personnel, their reliability makes them essential for confirming a diagnosis, especially in severe and asymptomatic cases.
While traditional PCR tests may take days, rapid molecular options are now available, providing results within minutes. This innovation presents a valuable solution for areas with limited resources or high testing demands, ensuring quicker identification and isolation of cases as per public health experts.
Antigen Testing: Fast but Less Accurate
Antigen tests, known for their rapid results, are often utilized for regular screenings in environments such as schools and workplaces. Despite offering quick answers, their sensitivity is lower compared to molecular tests, and multiple confirmations might be necessary to ensure accuracy according to the Mayo Clinic. This is particularly important when testing asymptomatic individuals or those with low viral loads.
Repeat antigen tests are recommended for accuracy. Users performing these tests at home should follow instructions closely and consider serial testing for reliable outcomes as suggested by Yale Medicine. This practice ensures a better chance of detecting an active infection.
The Significance of Antibody Tests
Antibody, or serology tests, focus on detecting the body’s immune response to the virus rather than the virus itself. These tests can provide insights into previous exposure but are not suitable for diagnosing active infections as stated by the FDA. They help in understanding the prevalence of past infections but do not inform on current contagiousness or protective immunity.
The Future of COVID-19 Testing
As the pandemic evolves, so do testing methods. Emerging technologies aim to enhance comfort and efficiency, with breath-based tests and pooled testing being explored by public health researchers. These methodologies may improve testing accessibility in under-resourced regions and contribute to more efficient management of COVID-19.
Another focus is on developing tests that better detect viral variants and measure infectivity. Innovative techniques, such as targeting multiple viral genome parts, promise enhanced accuracy in variant detection as per Yale Medicine findings. Though they require specialized labs, advancements like these signify promising strides toward comprehensive virus management.
Why You Should Learn More About COVID-19 Tests Today
Understanding the different types of COVID-19 tests is crucial for making informed decisions regarding health and safety. With ongoing developments in testing technology, awareness of each test’s strengths and limitations plays a key role in community health strategies.
By comprehending the scope and capabilities of available tests, individuals and policymakers can better manage the spread and impact of COVID-19. Staying informed about testing options, their applications, and emerging innovations ensures preparedness and enhances public health efforts in battling the pandemic.
Sources
Comprehensive Overview of COVID-19 Testing at Johns Hopkins Public Health
FDA’s Outline of COVID-19 Test Categories and Guidelines
CDC’s Criteria for COVID-19 Viral Testing