Crohn’s disease, a complex inflammatory condition affecting the digestive tract, reveals itself through a variety of symptoms that can be bewildering to those unfamiliar with the disease. These symptoms range from abdominal pain and diarrhea to systemic complications affecting multiple organs. Understanding these signs is vital not only for distinguishing this condition from other inflammatory bowel diseases but also for developing effective management strategies. Addressing both the physical and mental impacts of Crohn’s, this comprehensive exploration aims to illuminate paths toward improved quality of life.
Understanding Crohn’s Disease Symptoms
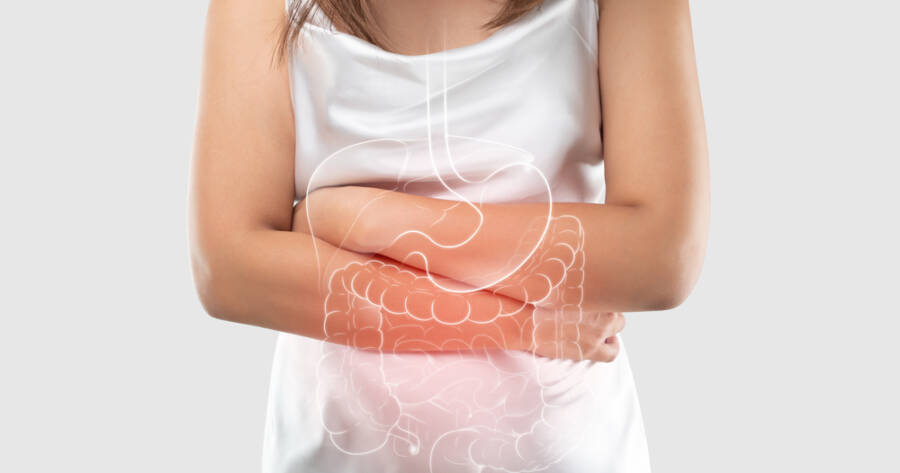
Crohn’s disease, a chronic inflammatory condition of the digestive tract, presents a range of symptoms which offer insight into its complex nature. Common symptoms, such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting, are indicative of gastrointestinal inflammation. These symptoms often affect appetite and lead to weight loss, anemia, and fatigue. Additionally, patients may experience sores in the mouth and anus as noted in studies on Crohn’s disease.
Understanding Crohn’s disease symptoms is essential to distinguish it from other forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), like ulcerative colitis. Unlike Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis pain typically localizes to the left side of the abdomen rather than being generalized. Additionally, perianal disease with symptoms such as swollen skin tags, abscesses, and fistulas appears more frequently in Crohn’s, sparking concerns over serious complications if left unchecked. The involvement of different types of Crohn’s disease depending on the areas affected further complicates its manifestation according to medical expertise.
Distinctive Symptoms and Complications
While Crohn’s disease shares symptoms with several other conditions, its specific indicators set it apart in the diagnostic process. Blood in stool, frequent diarrhea, joint pain, and fever are some early signs — progressing to steady symptoms that can exacerbate without medical intervention. Additionally, systemic complications can arise, impacting the joints, skin, eyes, and even the liver and kidneys. Persistent inflammation can also lead to local complications such as abscesses, fistulas, and strictures based on health reports. These reiterate the necessity of monitoring and addressing symptoms effectively to mitigate further health challenges.
Symptomatic relief for Crohn’s disease isn’t about curing it—there isn’t a cure—but involves managing and easing its symptoms. Treatments comprise a medley of anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, biologic medicines, and occasionally surgery. These interventions are tailored to reduce symptoms and maintain remission, ensuring that patients can live a high-quality and fulfilling life as indicated by digestive health agencies.
Identifying Risk Factors
Risk factors for developing Crohn’s disease range from genetic to lifestyle influences. Although the exact causes aren’t fully understood, smoking, environmental conditions, and stress are frequently cited contributors.
A significant portion of Crohn’s patients also reports familial ties, hinting at genetic predispositions where 20% have a family history of the disease. Lifestyle modifications like smoking cessation and stress management, paired with dietary adjustments, can contribute significantly to symptom management. These approaches aim to prevent flares and maintain remission according to scholarly studies.
Managing Mental and Physical Well-being
Crohn’s disease affects not only the body but also the mind. The chronic nature of the condition often leads to mental health concerns, such as depression and anxiety, which can adversely affect physical symptoms. Therefore, integrating mental health support, such as therapy and supportive group participation, is pivotal in addressing the full spectrum of Crohn’s’ impacts. Creating a support network through therapists and groups provides a necessary outlet for the emotional toll of chronic illness as emphasized in Crohn’s disease research.
Daily habits, including dietary regulation and stress management, complement medicines to alleviate symptoms and promote a balanced lifestyle. Exercise, ample hydration, and avoiding known dietary triggers are practical self-care strategies that help manage and reduce the strain of Crohn’s disease, crucial to living a balanced life.
Why You Should Learn More About Crohn’s Disease Symptoms Today
Having a comprehensive understanding of Crohn’s disease symptoms is invaluable for diagnosis and management. Recognizing the nuanced symptoms and their implications encourages early intervention, significantly improving chronic condition outcomes. This understanding guides treatment decisions, adapting them to enhance life quality while maintaining symptom remission.
Continued research, support groups, and informative resources equip individuals with knowledge, connecting them with experts and peers to navigate Crohn’s effectively. Engaging with such resources enables patients and loved ones to foster meaningful improvements in daily living and long-term health.